The liver is the largest organ in the body, so its diseases – especially cirrhosis, need particular attention as they pose a serious threat to your health. So, what is cirrhosis, and what should be done to diagnose the disease?

1. What Is Cirrhosis?
When the liver is damaged, its automatic response is to try to mend any damage and begin the recovery process, leading to liver fibrosis (cirrhosis), also known as scar tissue. The greater the extent of damage, the more scar tissue will form, increasing the degree of obstruction to the liver’s activities.
The scar tissue formed from cirrhosis blocks the flow of blood through the liver and slows down the processing of nutrients and toxins.
Cirrhosis, when it reaches the end stage, can be life-threatening. Specifically, it is predicted that by 2025, there will be 60,000 cirrhosis patients, 25,000 liver cancer patients, and 40,000 deaths in Vietnam (according to the Scientific Workshop on Strengthening Treatment Capacity and Prevention, hepatitis B virus, 2021).
Cirrhosis is classified into 2 types:
Compensated Cirrhosis
Compensated cirrhosis is the early stage of cirrhosis, which occurs when the liver has been damaged but is still able to maintain its functions. Therefore, compensated cirrhosis has no specific symptoms at the onset of the disease.
However, if you do not perform screening to detect the disease early, the liver can worsen each day, resulting in unpredictable consequences.

Decompensated Cirrhosis
Unlike compensated cirrhosis, decompensated cirrhosis is the later stage of cirrhosis when extensive damage is present. At this time, the liver function has lost its ability to function, the signs are easy to see, and the complications are extremely dangerous, especially liver cancer.
At this stage, the person will need to focus on treating symptoms and preventing complications.
2. Why Cirrhosis?
In Vietnam, cirrhosis is caused by two main causes:
Alcoholism
Wine and beer are popular drinks for Vietnamese people, especially indispensable at men’s drinking tables. However, excessive alcohol consumption leads to abuse and can cause liver cell damage in the following stages; fatty liver, chronic hepatitis, and finally, cirrhosis.
Viral Hepatitis Infection
Currently, there are 5 types of viruses that cause hepatitis, namely hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. Long-term hepatitis leads to cirrhosis, so viral hepatitis is considered a cause of cirrhosis.
In Vietnam, hepatitis B and C account for the highest rates of infection among viruses, with the number of chronically infected people being 7.8 million and 1 million, respectively (according to the Ministry of Health of Vietnam, in 2022).
– Hepatitis B: An inflammation of the liver caused by a type B virus, which is composed of a DNA molecule that causes acute or chronic disease (lasting for more than 6 months). Chronic hepatitis B, if left untreated, can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. This virus is transmitted through secretions such as saliva, blood, and vaginal fluids. In addition, it can also be transmitted from mother to child. The disease is preventable by vaccination but not for people who are currently infected with the hepatitis B virus or have been previously.

>>You may need: Viral Hepatitis Test Panel
– Hepatitis C: An inflammation of the liver caused by the type C virus, which is composed of RNA molecules and is usually chronic (lasting for more than 6 months). Hepatitis C, if left untreated, can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Currently, there is no way to prevent the disease.
Besides the above causes, cirrhosis also can form from drug abuse, genetics, or from diseases that have occurred in the liver and lead to complications.
3. Who Is Predisposed to Cirrhosis?
When you have cirrhosis, even in the early/late stages, your body will give you signs that something is not right. You need to pay close attention to these symptoms and risk factors:

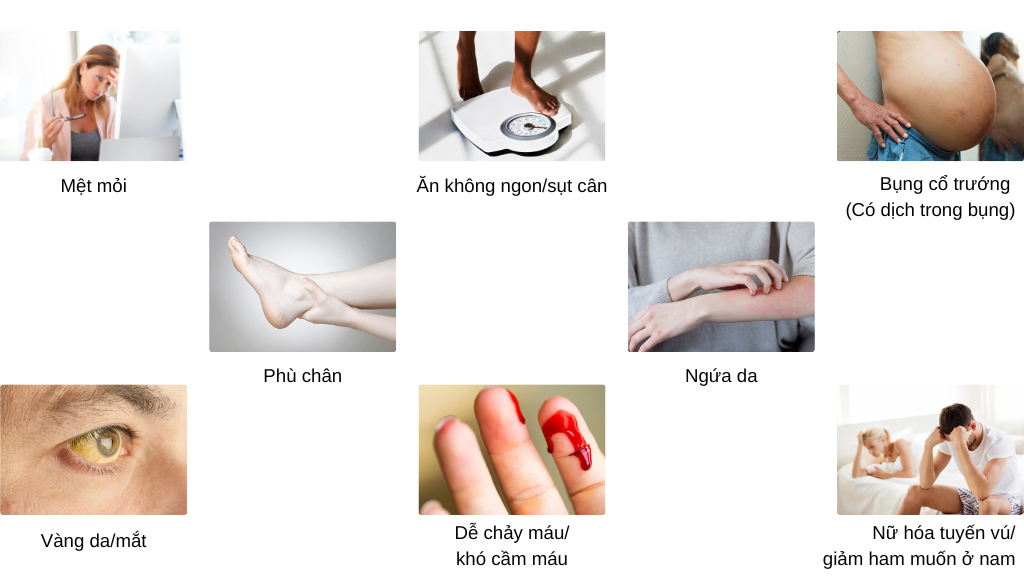
4. What Are The Symptoms Of Cirrhosis?
The most common clinical manifestations of cirrhosis include:
 5. How To Detect Cirrhosis?
5. How To Detect Cirrhosis?
General health check
Because the signs of cirrhosis are not always clear and it is easy to confuse with other diseases, you need to actively screen for the disease by having a regular check-up every 6-12 months.
This not only helps you detect liver diseases but also monitors your health to build or adjust lifestyle habits to protect your health.
Abdominal Ultrasound/Fibroscan
Abdominal ultrasounds help to visualize the morphology of the liver, while Fibroscans help to assess the degree of fibrosis and steatosis of the liver. Fibroscan is the “gold standard” in the diagnosis of cirrhosis at the present time.
Liver Test
You need to have liver tests done, typically liver enzyme tests (ALAT + ASAT), or tests for hepatitis B and C. Accordingly, you will be asked to draw blood. The doctor will then rely on the test indicators to diagnose any condition and assess the function of the liver.
A liver test is an essential activity to help you and your doctor evaluate the condition of your liver, allowing an effective treatment and prevention regimen and reducing the risk of cancer.
To make it easier for you to carry out tests to screen for liver diseases, as well as close out the last days of the Year of the Tiger 2022 with a lot of joy, Diag presents the first 500 customers with a special “Review” price of 0 dong”.
 (*) Note:
(*) Note:
Only applicable to customers who register directly and collect samples at 3 Diag sampling branches, including:
– Diag Cu Chi: 39 provincial road 8, Cu Chi town, Ho Chi Minh City;
– Diag Hoc Mon: 31/5 Quang Trung Street, Hoc Mon Town, Ho Chi Minh City;
– Diag Can Tho: 44 – 46 April 30th Street, An Phu Ward, Ninh Kieu District, Can Tho City.
Immediately go to one of the above 3 branches to take samples for testing and perform “Test 0 VND” to prepare for a healthy start to the new year. Don’t hesitate to call the hotline on 1900 1717 for 24/7 consultation with the dedicated staff at Diag!
* The article is based upon consultation with medical experts of Diag. However, the above information is for reference only and is not a substitute for medical advice. Before taking any action based on the information provided, please get advice from a medical professional.

 1900 1717
1900 1717